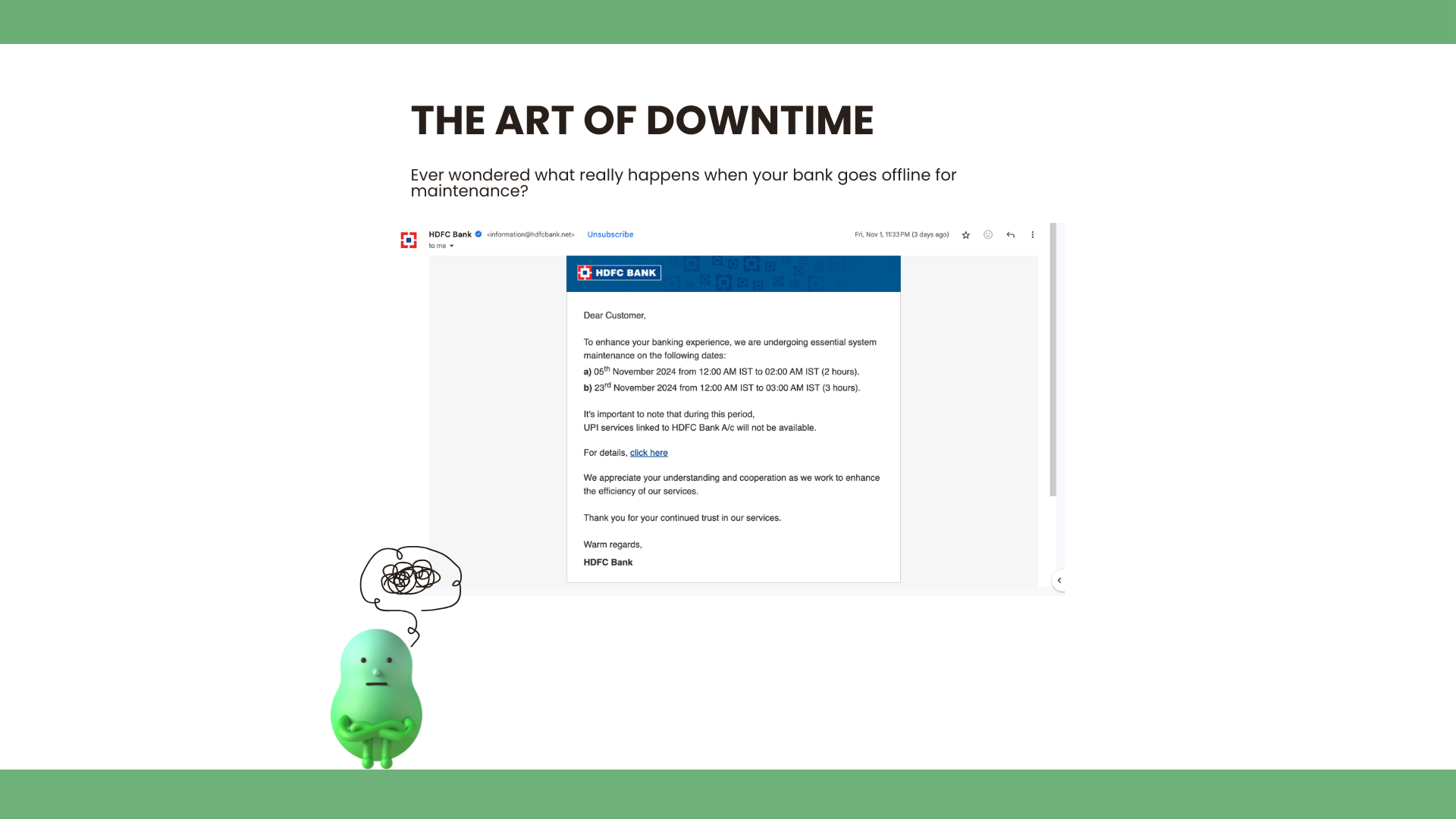
Ever wondered what really happens when your bank goes offline for maintenance? You see a polite email—“Scheduled Maintenance Downtime”—and suddenly your online banking, mobile app, and ATM services vanish behind a “Please check back later” banner. It feels like a brief blackout in an otherwise 24/7 world. Curious, I decided to dig a little deeper and found out that planned downtime is anything but idle time—it’s a carefully orchestrated operation.
1. The Email That Started It All
When I received that maintenance notice, I pictured technicians in white coats tinkering at random. The reality is far more disciplined. Banks schedule downtime windows weeks or even months in advance. They choose low-traffic hours—often late nights or weekends—to minimize impact. Then they lock it in, sending alerts by email, SMS, and even in-app notifications so customers know exactly when services will pause.
2. Preparation: The Secret Sauce
Behind the scenes, downtime prep feels like staging a Broadway show:
- Rehearsals (Staging Environments): Before touching live systems, every change runs through identical test setups. Engineers deploy to staging servers, run automated tests, and even simulate peak loads to catch surprises early.
- Runbooks & Checklists: Detailed step-by-step guides ensure each task—applying a patch, migrating a database, flipping a feature flag—follows the same proven sequence. No one improvises on opening night.
- Change Approval Boards: Every planned change gets reviewed by a panel of architects, security experts, and operations leads. They weigh risks, rollback plans, and dependencies before giving the green light.
This preparation phase can take weeks of planning and dry-runs, all to guarantee that the actual downtime window is as brief and predictable as possible.
3. Downtime in Action: A Tight Choreography
When the clock strikes maintenance time, the bank switches from “live” to “maintenance” mode:
- Freeze Transactions: New customer requests are blocked or queued.
- Database Snapshots: Engineers take final backups, ensuring they can restore data if something goes awry.
- Deploy & Migrate: Software patches, security updates, or schema changes roll out across multiple servers—often in parallel to shave off precious minutes.
- Smoke Tests: Automated health checks verify that critical services—logins, transfers, balance inquiries—are up and running correctly.
- Go/No-Go Decision: If all tests pass, the maintenance mode lifts. If not, operators trigger rollback procedures documented in the runbook.
Remarkably, banks aim to complete all these steps within just a few hours—or even a single hour—so customer impact is minimal.
4. The Role of Automation
Manual work slows you down and introduces human error. That’s why modern banks rely heavily on automation:
- CI/CD Pipelines: Continuous Integration and Deployment systems package and test code automatically, then trigger deployments to maintenance servers with a single command.
- Infrastructure as Code: Server configurations, database migrations, and network rules are defined in version-controlled scripts, ensuring consistency across environments.
- Automated Rollbacks: If a post-deployment check fails, scripts detect the issue and roll the system back to the previous stable state without manual intervention.
- Monitoring & Alerts: Real-time dashboards track every step, and any anomaly—disk space running low, a service failing to start—triggers instant alerts so engineers can jump in before customers notice.
With these automation layers, what once took days of manual labor now fits into a two-hour maintenance window.
Conclusion
Maintaining a high-availability service isn’t about avoiding downtime—it’s about mastering it. Banks transform a momentary service pause into a polished performance through meticulous planning, rigorous testing, and advanced automation. The next time you see that “Scheduled Maintenance” notice, know that an entire orchestra of tools and teams has rehearsed every note, all to bring your banking services back online without missing a beat.